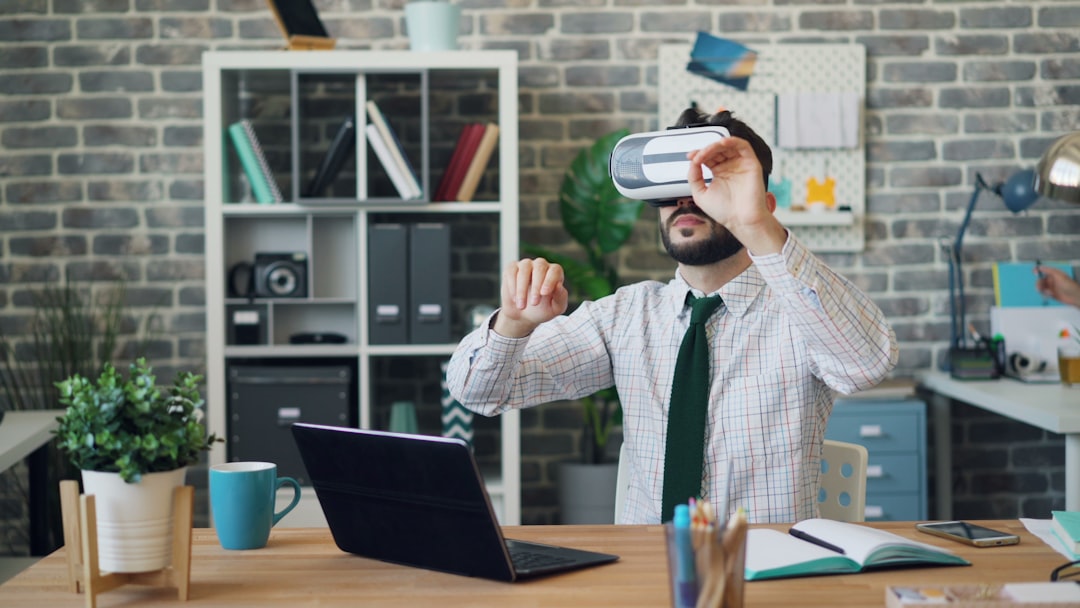
Immersive Virtual Reality (IVR) represents a groundbreaking evolution in the realm of digital experiences, transcending traditional boundaries of interaction and engagement. By creating a simulated environment that can be similar to or completely different from the real world, IVR allows users to immerse themselves in a three-dimensional space where they can interact with virtual elements in a seemingly tangible manner. This technology employs sophisticated hardware, such as headsets and motion sensors, to deliver a sensory experience that engages sight, sound, and even touch.
As a result, users can explore virtual landscapes, manipulate objects, and engage in activities that would be impossible or impractical in the physical world. The allure of IVR lies not only in its ability to transport users to fantastical realms but also in its potential to enhance learning, training, and entertainment. The rise of immersive virtual reality has been fueled by advancements in computing power, graphics rendering, and user interface design.
As these technologies have matured, they have made it possible for developers to create increasingly realistic and interactive environments. The gaming industry was among the first to embrace IVR, offering players an unparalleled level of engagement that traditional gaming formats could not match. However, the applications of IVR extend far beyond entertainment; they encompass fields such as education, healthcare, architecture, and even social interaction.
As society becomes more interconnected through digital platforms, the demand for immersive experiences that foster deeper connections and understanding is likely to grow. This article will explore the multifaceted impact of immersive virtual reality on digital experiences, its advantages across various industries, the challenges it faces, and its future trajectory.
Key Takeaways
- Immersive virtual reality (VR) technology creates a simulated environment that allows users to interact with a 3D world.
- Immersive VR has the potential to revolutionize digital experiences by providing a more engaging and realistic environment for users.
- Various industries, including healthcare, education, and entertainment, can benefit from immersive VR technology by enhancing training, education, and customer experiences.
- Challenges and limitations of immersive VR technology include high costs, technical limitations, and potential negative health effects.
- The future of immersive VR technology holds promise for continued advancements in hardware, software, and user experiences, shaping the digital landscape.
The Impact of Immersive Virtual Reality on Digital Experiences
The impact of immersive virtual reality on digital experiences is profound and multifaceted, fundamentally altering how individuals interact with technology and each other. One of the most significant changes is the shift from passive consumption of content to active participation. In traditional media formats, users often remain spectators, absorbing information without any real engagement.
In contrast, IVR invites users to step into the narrative, allowing them to influence outcomes and explore environments at their own pace. This level of interactivity fosters a deeper emotional connection to the content, enhancing retention and understanding. For instance, educational programs utilizing IVR can simulate historical events or complex scientific concepts, enabling students to experience lessons firsthand rather than merely reading about them in textbooks.
Moreover, immersive virtual reality has the potential to revolutionize social interactions in digital spaces. As people increasingly seek meaningful connections online, IVR offers a platform for shared experiences that mimic real-life interactions. Virtual gatherings can take place in stunningly rendered environments where participants can engage with one another through avatars, share experiences, and collaborate on projects.
This capability is particularly valuable in a world where remote work and virtual communication have become the norm. By providing a sense of presence and community that traditional video conferencing tools lack, IVR can help bridge the gap between physical distance and emotional connection. As these technologies continue to evolve, they will undoubtedly shape how we perceive and engage with digital experiences.
Advantages of Immersive Virtual Reality in Various Industries

The advantages of immersive virtual reality span a wide array of industries, each harnessing its unique capabilities to enhance processes and outcomes. In education, for example, IVR offers an innovative approach to learning that caters to diverse learning styles. Students can engage with complex subjects through interactive simulations that allow them to visualize concepts in three dimensions.
This hands-on approach not only makes learning more enjoyable but also improves comprehension and retention rates. Furthermore, IVR can facilitate remote learning by providing students with access to virtual classrooms and resources that might otherwise be unavailable due to geographical constraints. In the realm of healthcare, immersive virtual reality is proving to be a game-changer in both training and patient care.
Medical professionals can utilize IVR for surgical simulations that replicate real-life scenarios without the risks associated with live procedures. This training method enhances skill acquisition and confidence among practitioners while ensuring patient safety. Additionally, IVR is being employed as a therapeutic tool for patients dealing with anxiety disorders or phobias.
By immersing individuals in controlled virtual environments where they can confront their fears gradually, therapists can help patients develop coping strategies in a safe space. The versatility of IVR across various sectors underscores its potential to drive innovation and improve outcomes.
Challenges and Limitations of Immersive Virtual Reality
| Challenges and Limitations of Immersive Virtual Reality |
|---|
| 1. Motion Sickness |
| 2. Limited Field of View |
| 3. Cost of Equipment |
| 4. Health and Safety Concerns |
| 5. Technical Complexity |
| 6. Content Development Challenges |
Despite its numerous advantages, immersive virtual reality faces several challenges and limitations that must be addressed for it to reach its full potential. One significant hurdle is the accessibility of the technology itself. High-quality VR headsets and equipment can be prohibitively expensive for many consumers and organizations, creating a barrier to entry that limits widespread adoption.
Additionally, the technical requirements for running immersive applications often necessitate powerful computers or consoles, further complicating access for those without the means to invest in such technology. As a result, there is a risk that IVR could exacerbate existing inequalities in access to education and training opportunities. Another challenge lies in the potential for motion sickness and discomfort experienced by some users during immersive experiences.
The disconnect between visual input and physical movement can lead to symptoms such as dizziness or nausea, which may deter individuals from engaging with IVR technologies altogether. Developers are actively working on solutions to mitigate these issues through improved design practices and user interface adjustments; however, finding a one-size-fits-all solution remains elusive. Furthermore, as immersive experiences become more realistic and engaging, concerns about addiction and escapism may arise.
Striking a balance between leveraging the benefits of IVR while ensuring responsible usage will be crucial as this technology continues to evolve.
The Future of Immersive Virtual Reality Technology
Looking ahead, the future of immersive virtual reality technology appears promising yet complex as it continues to evolve at an unprecedented pace. Innovations in hardware are expected to make VR headsets lighter, more comfortable, and more affordable while enhancing visual fidelity and responsiveness. As these advancements occur, we may witness an increase in consumer adoption across various demographics, leading to a broader range of applications beyond gaming and entertainment.
Industries such as real estate could leverage IVR for virtual property tours, allowing potential buyers to explore homes from anywhere in the world without ever stepping foot inside them. Moreover, as artificial intelligence (AI) becomes increasingly integrated into immersive experiences, we can anticipate more personalized interactions within virtual environments. AI-driven avatars could respond dynamically to user behavior and preferences, creating tailored experiences that adapt in real-time.
This level of customization could enhance training programs by providing feedback based on individual performance or adjusting difficulty levels according to user proficiency. Additionally, advancements in haptic feedback technology may allow users to experience tactile sensations within virtual spaces, further blurring the lines between reality and simulation. As these innovations unfold, they will undoubtedly shape the trajectory of immersive virtual reality technology for years to come.
Ethical and Social Implications of Immersive Virtual Reality

As immersive virtual reality technology continues to advance and permeate various aspects of daily life, it brings forth a host of ethical and social implications that warrant careful consideration. One pressing concern is the potential for desensitization or altered perceptions of reality among users who frequently engage with hyper-realistic virtual environments. Prolonged exposure to simulated experiences may lead individuals to develop skewed understandings of social interactions or emotional responses when faced with real-world situations.
This phenomenon raises questions about the responsibility of developers in creating content that promotes healthy engagement rather than fostering harmful behaviors or unrealistic expectations. Additionally, issues surrounding privacy and data security become increasingly relevant as users navigate immersive environments that often require personal information for customization or social interaction purposes. The collection and storage of user data pose significant risks if not managed responsibly; breaches could expose sensitive information or lead to misuse by third parties.
Furthermore, as virtual spaces become more integrated into social dynamics—such as online communities or workplaces—questions about inclusivity and representation arise. Ensuring diverse voices are heard in the development process is essential for creating equitable experiences that reflect the richness of human experience rather than perpetuating stereotypes or biases.
The Potential of Immersive Virtual Reality in Shaping Digital Experiences
In conclusion, immersive virtual reality holds immense potential for shaping digital experiences across various domains while simultaneously presenting challenges that must be navigated thoughtfully. Its ability to transform passive engagement into active participation has already begun redefining how we learn, work, and connect with one another in an increasingly digital world. As industries continue to explore innovative applications—from education to healthcare—IVR stands poised to revolutionize traditional practices by offering new avenues for interaction and understanding.
However, as we embrace this transformative technology, it is crucial to remain vigilant about its ethical implications and societal impact. By fostering responsible development practices that prioritize accessibility, inclusivity, and user well-being, we can harness the power of immersive virtual reality while mitigating potential risks associated with its use. Ultimately, as we look toward the future of IVR technology—marked by advancements in hardware capabilities and AI integration—we must strive for a balanced approach that maximizes its benefits while addressing the complexities inherent in this exciting frontier of digital experience.
If you’re interested in learning more about the applications and implications of virtual reality, you might find the content on Bongoc’s website enlightening. Specifically, their “About Us” page provides insights into how they incorporate cutting-edge technologies like VR into their projects. For more detailed information, you can visit their page directly at https://bongoc.top/about-us/. This resource could be particularly useful if you’re curious about the innovative approaches companies are taking with virtual reality in various industries.
FAQs
What is Virtual Reality (VR)?
Virtual Reality (VR) is a computer-generated simulation of an environment that can be interacted with in a seemingly real or physical way by a person using special electronic equipment, such as a helmet with a screen inside or gloves fitted with sensors.
How does Virtual Reality work?
Virtual Reality works by using computer technology to create a simulated environment. This environment can be experienced through a VR headset, which tracks the user’s head movements and adjusts the display accordingly to create a sense of immersion and presence in the virtual world.
What are the applications of Virtual Reality?
Virtual Reality has a wide range of applications, including entertainment (such as gaming and immersive experiences), education (virtual field trips and training simulations), healthcare (pain management and therapy), architecture and design (virtual walkthroughs and modeling), and more.
What are the different types of Virtual Reality devices?
There are several types of Virtual Reality devices, including tethered VR headsets (connected to a computer or gaming console), standalone VR headsets (with built-in processing power), and mobile VR headsets (using a smartphone as the display and processing unit).
What are the potential benefits of Virtual Reality?
Virtual Reality has the potential to offer benefits such as enhanced learning experiences, improved training simulations, immersive entertainment, therapeutic applications, and new ways of experiencing and interacting with digital content.
What are the challenges of Virtual Reality?
Challenges of Virtual Reality include issues related to motion sickness, the high cost of quality VR equipment, the need for powerful computing hardware, and concerns about potential negative effects on physical and mental health from prolonged use.