Data science is an interdisciplinary field that combines various techniques from statistics, mathematics, and computer science to extract meaningful insights from structured and unstructured data. At its core, data science involves the collection, analysis, and interpretation of vast amounts of information to uncover patterns, trends, and correlations that can inform decision-making processes. The discipline has gained significant traction in recent years, driven by the exponential growth of data generated by digital interactions, social media, and IoT devices.
As organizations increasingly recognize the value of data-driven insights, the demand for skilled data scientists has surged, making it one of the most sought-after professions in the modern job market. The foundational elements of data science encompass a range of methodologies and tools designed to facilitate the analysis of complex datasets. This includes statistical analysis, machine learning algorithms, data mining techniques, and data visualization methods.
By employing these techniques, data scientists can transform raw data into actionable intelligence that can drive strategic initiatives across various sectors. Furthermore, the iterative nature of data science allows for continuous improvement and refinement of models, enabling organizations to adapt to changing market conditions and consumer behaviors. As a result, understanding the basics of data science is essential for anyone looking to leverage the power of data in today’s information-driven landscape.
Key Takeaways
- Data science involves analyzing and interpreting complex data to make informed decisions and predictions.
- Data science plays a crucial role in helping businesses and industries make strategic decisions and improve operations.
- Big data has the potential to provide valuable insights and opportunities for businesses when harnessed effectively.
- Data science has a significant impact on decision making by providing accurate and actionable insights from data analysis.
- Various tools and technologies, such as machine learning and data visualization, are essential for data science processes and analysis.
- Ethical considerations in data science, such as privacy and bias, are important to address for responsible and fair data usage.
- The future of data science holds implications for various industries, including advancements in AI and automation.
The Role of Data Science in Business and Industry
In the contemporary business environment, data science plays a pivotal role in shaping strategies and enhancing operational efficiency. Organizations across various industries are harnessing the power of data analytics to gain a competitive edge, optimize processes, and improve customer experiences. For instance, retail companies utilize predictive analytics to forecast inventory needs based on consumer purchasing patterns, thereby minimizing waste and maximizing sales opportunities.
Similarly, financial institutions employ risk assessment models powered by data science to evaluate creditworthiness and detect fraudulent activities, ultimately safeguarding their assets and ensuring regulatory compliance. Moreover, the integration of data science into business operations fosters a culture of informed decision-making. By relying on empirical evidence rather than intuition or anecdotal experiences, organizations can make more accurate predictions about market trends and customer preferences.
This shift towards data-driven decision-making not only enhances operational effectiveness but also promotes innovation by enabling companies to identify new opportunities for growth. As businesses continue to evolve in an increasingly digital landscape, the role of data science will only become more pronounced, driving advancements in automation, personalization, and overall strategic planning.
Harnessing the Potential of Big Data

The advent of big data has revolutionized the way organizations approach data analysis and decision-making. Big data refers to the vast volumes of structured and unstructured information generated at unprecedented speeds from various sources such as social media, sensors, and transactional systems. This wealth of information presents both challenges and opportunities for businesses seeking to harness its potential.
By employing advanced analytics techniques, organizations can sift through massive datasets to uncover valuable insights that were previously hidden or inaccessible. To effectively harness big data, organizations must invest in robust infrastructure and analytical capabilities. This includes adopting cloud computing solutions that provide scalable storage options and powerful processing capabilities to handle large datasets efficiently.
Additionally, leveraging machine learning algorithms allows businesses to automate the analysis process, enabling them to identify patterns and trends in real-time. As companies become more adept at utilizing big data analytics, they can enhance their operational efficiency, improve customer engagement, and drive innovation across their product offerings. Ultimately, the ability to harness big data will be a defining factor for organizations striving to remain competitive in an increasingly data-centric world.
The Impact of Data Science on Decision Making
| Metrics | Impact |
|---|---|
| Accuracy | Improved accuracy in decision making through data-driven insights |
| Efficiency | Streamlined decision-making processes through data analysis and automation |
| Risk Management | Better identification and mitigation of risks through predictive analytics |
| Innovation | Encouragement of innovation and creativity in decision making based on data trends |
| Cost Reduction | Reduction of unnecessary expenses by making data-informed decisions |
Data science has fundamentally transformed the landscape of decision-making within organizations by providing leaders with actionable insights derived from comprehensive analyses. Traditional decision-making processes often relied on intuition or historical precedents; however, the integration of data science allows for a more empirical approach that minimizes biases and enhances accuracy. By utilizing predictive modeling and statistical analysis, decision-makers can evaluate potential outcomes based on various scenarios, leading to more informed choices that align with organizational goals.
Furthermore, the impact of data science extends beyond mere operational decisions; it also influences strategic planning at the highest levels of management. Executives can leverage insights from data analytics to identify emerging market trends, assess competitive landscapes, and allocate resources more effectively. This strategic foresight enables organizations to pivot quickly in response to changing conditions or capitalize on new opportunities as they arise.
As a result, the incorporation of data science into decision-making processes not only enhances organizational agility but also fosters a culture of continuous improvement driven by evidence-based practices.
The Tools and Technologies of Data Science
The field of data science is supported by a diverse array of tools and technologies that facilitate the collection, analysis, and visualization of data. Programming languages such as Python and R have become staples among data scientists due to their extensive libraries and frameworks designed for statistical analysis and machine learning. These languages enable practitioners to build complex models and perform sophisticated analyses with relative ease.
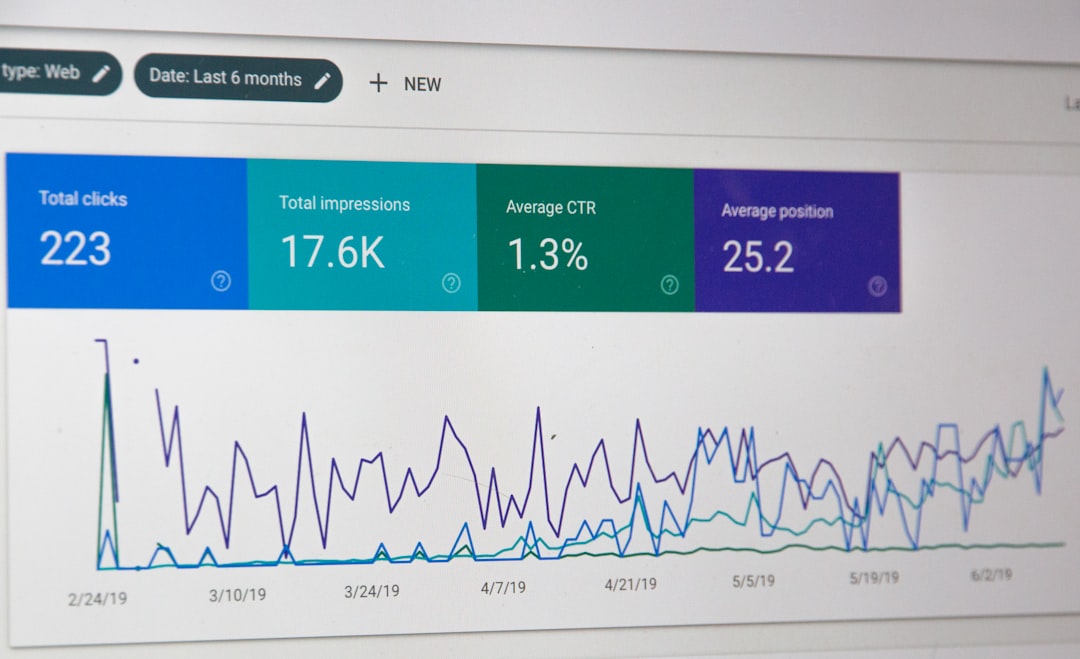
Additionally, platforms like Apache Hadoop and Spark provide powerful frameworks for processing large datasets across distributed computing environments, making them essential for handling big data challenges. In addition to programming languages and processing frameworks, visualization tools play a crucial role in communicating insights derived from data analyses. Software such as Tableau and Power BI allows users to create interactive dashboards that present complex information in an easily digestible format.
These visualizations not only enhance understanding but also facilitate collaboration among stakeholders by providing a common platform for discussing findings and implications. As technology continues to evolve, the tools available to data scientists will become increasingly sophisticated, enabling them to tackle more complex problems and derive deeper insights from their analyses.
The Ethical Considerations of Data Science

Privacy and Consent Concerns
The collection and analysis of personal data raise significant concerns regarding privacy and consent. Organizations must navigate complex legal frameworks governing data protection while ensuring that they respect individuals’ rights to privacy.
Bias in Algorithms and Discriminatory Outcomes
Moreover, the potential for bias in algorithms poses another ethical challenge; if not carefully managed, biased datasets can lead to discriminatory outcomes that disproportionately affect marginalized groups. To address these ethical dilemmas, it is essential for organizations to adopt transparent practices that prioritize accountability in their data science initiatives.
Building Trust through Ethical Awareness and Governance
Additionally, fostering a culture of ethical awareness among data scientists can help mitigate risks associated with bias and privacy violations. By prioritizing ethical considerations in their work, organizations can build trust with stakeholders while ensuring that their data-driven initiatives contribute positively to society as a whole.
The Future of Data Science and its Implications
Looking ahead, the future of data science is poised for remarkable growth and transformation as technological advancements continue to reshape the landscape. The proliferation of artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning will further enhance the capabilities of data scientists, enabling them to develop more sophisticated models that can analyze complex datasets with greater accuracy. As these technologies become more accessible, organizations across various sectors will increasingly rely on automated analytics solutions to drive decision-making processes.
Moreover, as the volume of available data continues to expand exponentially, the demand for skilled professionals in the field will only intensify. Educational institutions are already adapting their curricula to prepare students for careers in data science by emphasizing practical skills in programming, statistics, and machine learning. This shift will ensure a steady pipeline of talent equipped to tackle emerging challenges in an ever-evolving digital landscape.
Ultimately, the implications of these developments will extend beyond individual organizations; as data science becomes more ingrained in society’s fabric, it will shape industries, influence public policy decisions, and redefine how we understand our world through the lens of data-driven insights.
If you’re delving into the world of Data Science and looking for more information on how data is managed and utilized on websites, it might be beneficial to understand the underlying policies that govern data usage. A good starting point could be reviewing the Cookie Policy of a website, which outlines how data is collected through cookies. This can provide insights into data privacy, user tracking, and how data analytics play a role in enhancing user experience on digital platforms.
FAQs
What is data science?
Data science is a multidisciplinary field that uses scientific methods, processes, algorithms, and systems to extract knowledge and insights from structured and unstructured data.
What are the key skills required for a career in data science?
Key skills required for a career in data science include programming (Python, R, SQL), statistical analysis, machine learning, data visualization, and domain knowledge in the specific industry.
What are the common tools and technologies used in data science?
Common tools and technologies used in data science include programming languages (Python, R), data visualization tools (Tableau, Power BI), machine learning libraries (TensorFlow, scikit-learn), and big data technologies (Hadoop, Spark).
What are the applications of data science in various industries?
Data science has applications in various industries such as healthcare (predictive analytics for patient outcomes), finance (fraud detection and risk assessment), e-commerce (recommendation systems), and marketing (customer segmentation and targeting).
What is the process of data science project lifecycle?
The data science project lifecycle typically involves problem definition, data collection, data cleaning and preprocessing, exploratory data analysis, model building, model evaluation, and deployment of the solution.
What are the ethical considerations in data science?
Ethical considerations in data science include privacy concerns, bias in algorithms, transparency in decision-making, and the responsible use of data for societal benefit.